Server Infrastructure
Server
Tower-Type Server : This is a server that looks like a vertical machine. It is similar to an office desktop PC. It is suitable for locations without a dedicated server rack. It is a great choice for office/branch offices. Small and medium or home office and this type of server will be cheaper than other types of server with the same specification.

Rackmount-Type Server: This is a server that designed to be installed in a rack cabinet to save space in placement and orderly. This type of server suitable for datacenter.
Storage
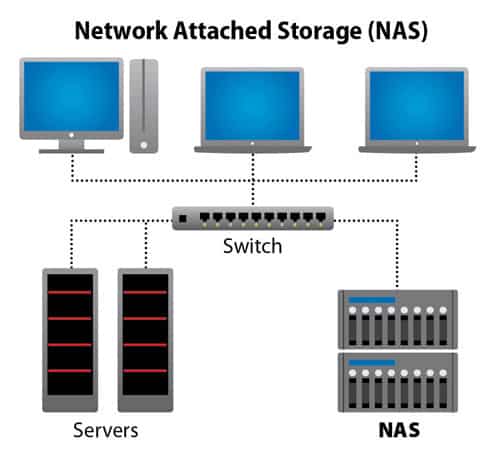
Network Attach Storage (NAS) : Storage that works like a server that connects to a network via a LAN switch same as a regular server and it can connect to a wireless network. This type of storage used as a File Server to share various data files over the network to users or used as a storage for applications that do not require high I/O
Types of workload that suitable for using NAS are:
- Storage for backup data.
- Closed-Circuit Television camera (CCTV).
- File sharing (File Server)
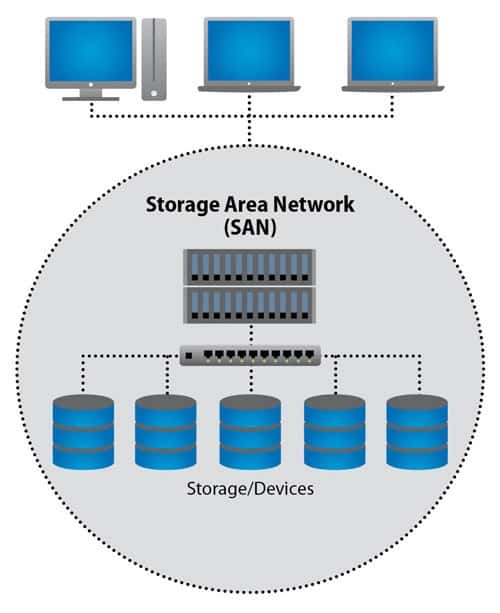
Storage Area Network (SAN) : This is a storage that has better performance than NAS and can expand more storage space. SAN can be connected to multiple servers by connect through SAN Switch, which is a separate interface from LAN. Generally SAN uses a Fiber Channel (FC) interface, which is high speed that can transmit data faster and high performance. SAN is suitable for applications that require availability, reliable and high performance
Types of workload that suitable for using SAN are:
- High Performance Computing
- Store large and complex databases
- Virtualization / Cloud Data Center
- Video Editing
Tape Cartridge : It is type of data stores in the format of a roll of tape which relies on Tape Drive or Tape Library which is controlled by the Backup Server to write and read the data. This type of storage is unsuitable for back up a big data because read and write rate is slower than other types of storage, However traditional tape-based storage is still in great demand because It’s a inexpensive and secure to protect and preserve information that you rarely access but it’s still necessary in the long term and this type of storage is meet requirements that require off-site backup.

VMWare
Virtualization Technology is a technology that simulates an entire computer or virtual machine under the same set of hardware. This technique allows a single server to act like multiple computers. Each machines work in parallel. and allows to run multiple operating systems at the same time and it is independent from the actual server, even if they are on different platforms, which helps organizations to use the resources of the server to the fullest. It will share resources of the main machine such as CPU, Memory, Hard Disk, etc. on single or multiple server machines to be able to install a large number of operating systems, software, applications and can still work simultaneously. Whether using the same platform or different platforms.
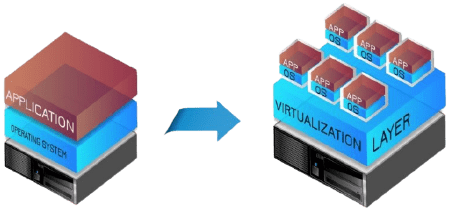
Benefits of Virtualization
Our services
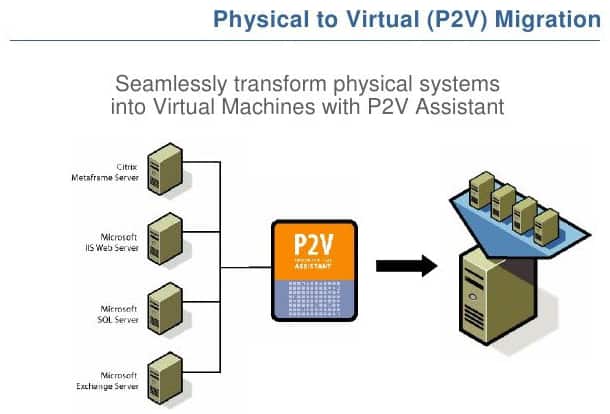
1. Migrate from Bare-metal or Physical Server to Virtualization This method is called P2V, which stands for Physical to Virtual. It installs server virtualization first, then converts the physical server into a virtual machine and imports it into the virtualization system.
2. Migrate from existing version to new version and hardware This method migrates the version to the new software version and new set of hardware, This method, customers must running server in virtualization environment before, Then can be migrating from the old version to the new version on the new set of hardware.
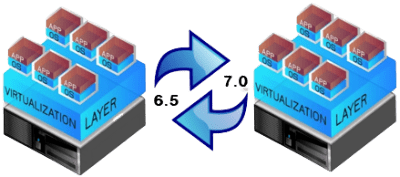
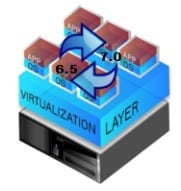
3. Upgrade from existing version to existing Hardware This method will upgrade the version from the original version that the customer is using to the new version on the same hardware. The version that can be upgraded depends on the hardware version that can be supported.
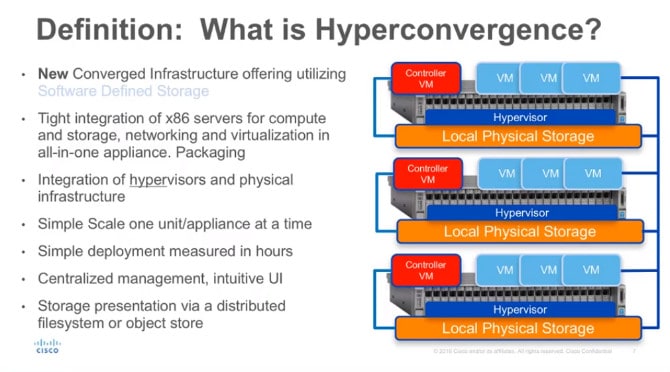
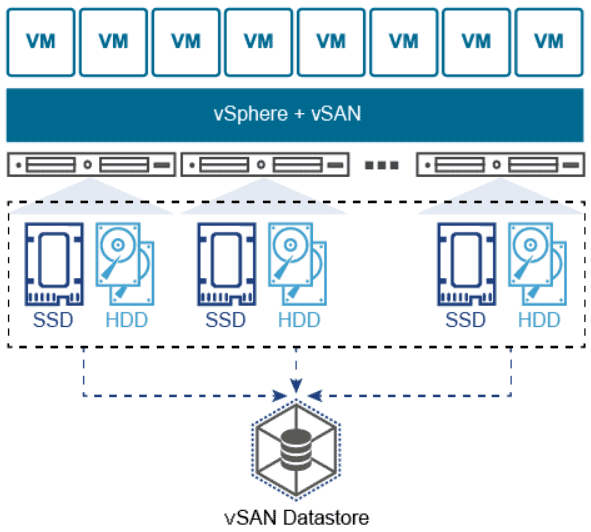
Hyper Converged Infrastructure (HCI)
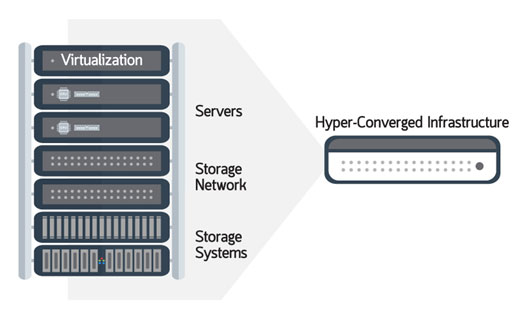
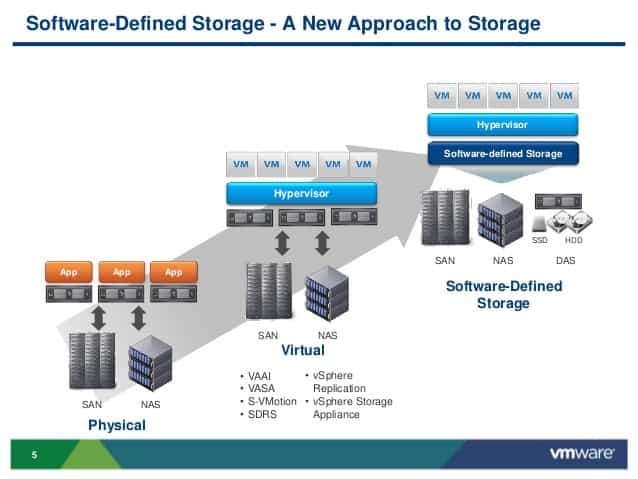
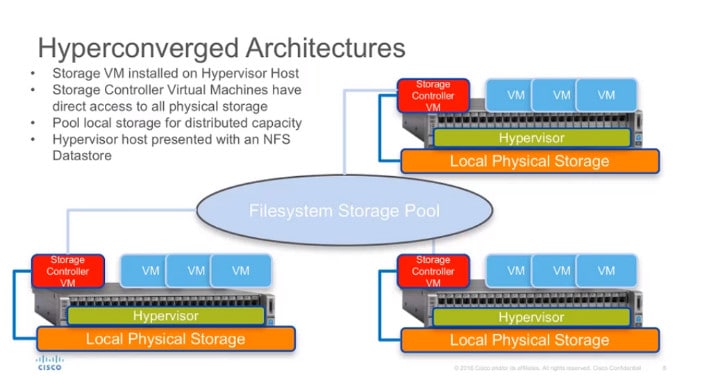
Hyper-Converge Infrastructure is the introduction of technology Hyper-Converged to combine IT Infrastructure, Server Storage and Network into one system. Can support scalability (Scalable) by using Software Defined to allow every hardware to connect to each other for running continuously. If any system has a problem Other systems can work instead.
1. Physical is a server that is clearly separated from each other. Each server connects to storage on the same SAN or NAS.
2. Virtual is a server that install on physical server that install hypervisor and used storage on the same SAN or NAS as physical server.
3. Software Defined Storage (SdS) (SdS) is technology that install hypervisor into physical server and installing Guest VMs to connect Storage on SAN, NAS or DAS, will reduce the risk of server when storage is broken that will make whole system crash. It will install hypervisor for example VMware ESXi or Microsoft Hyper-V on physical server and create a guest VM to install the software, then pull the disk from every server to make a storage pool using standard protocols. NFS and allow each server to share a storage pool. Server-to-server connections may be connected via Fiber Channels to achieve speeds. Most HCI uses 10Gb network, comparable to the storage interface transfer rate.
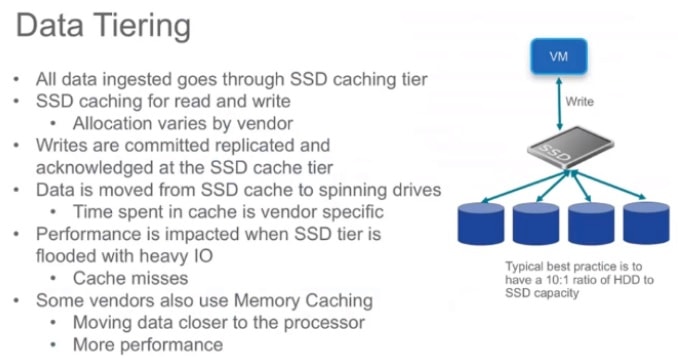
Data Tiering
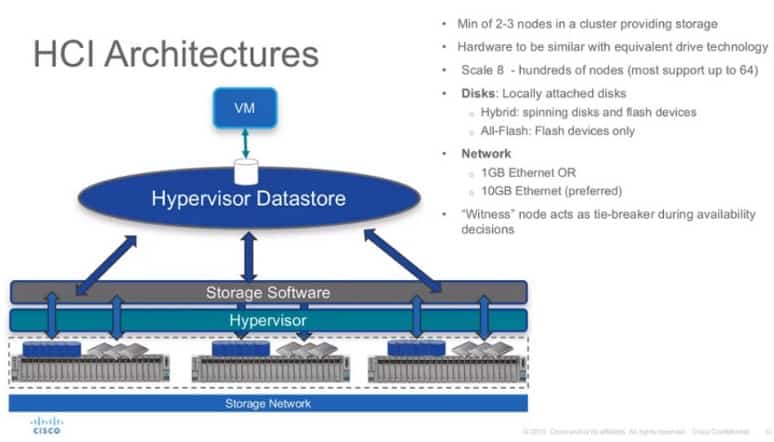
If doing it as a Hybrid, divide the Data Storage into 2 Tiering which are Cache The higher the cache, the higher the performance. All data is sent to the SSD caching both read and write. before going to actually write to the data storage Distributing HCI Data Hight Availability will use a distributed write method, for example, one set of data will write multiple copies, for example RF3 will divide the writes into 3 copies distributed to nodes. which no more RAID.
For Hybrid, divide the Data Storage into 2 Tiering which are
- Cache: High cache high performance. All data will sent into the SSD caching both read and write before actually write to the data storage.
- Distributing: HCI data high availability will use a distributed write method. For example, one set of data will write multiple copies, such as RF3 will divide the writes into 3 copies distributed to nodes which no more RAID
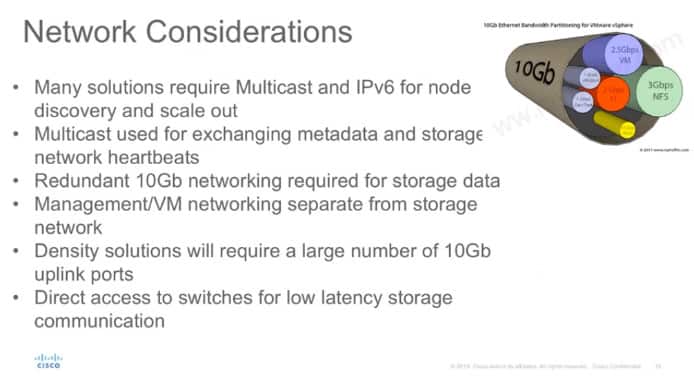
Network division, eg 3Gbps for NFS , 2.5Gbps for VM.